Esters of polyhydroxylated compounds (panthenol) are bioactive products of widespread application in the cosmetic and pharmaceutical industries due to their bioactive properties, such as humectant, moisturizing, anti-ageing, and wound-healing, among others. Despite the industrial interest in these products, very few synthetic approaches to obtain panthenol esters have been reported. Sustainability plays a fundamental role in the cosmetic and personal care industry, leading to the need for new production methods based on clean approaches.
Esters are currently obtained by chemical or enzymatic catalysis from derivatives of carboxylic acids, in reaction media based on organic solvents. These classical processes of organic synthesis are not very selective, and can also generate undesired products, which means that intensive purification of products is necessary. The situation leads to increased production costs, besides the generation of waste products that negatively affect the sustainability and green chemistry character of the production processes.
Researchers from the University of Murcia, and the Jaume I University have jointly developed a protocol for obtaining panthenol from enzymatic synthesis, this approach supposes a clean and useful process for the sustainable industrial scaling up of panthenol production.
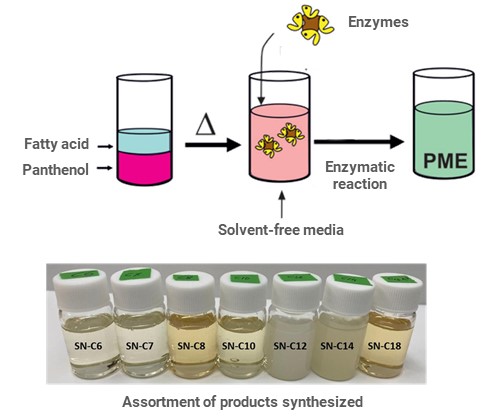
The process is carried out in organic solvent-free media, and it comprises the direct esterification reaction catalyzed by an enzyme. The addition of a biocatalyst to the eutectic mixture leads to the selective lypophilization of panthenol with free fatty acids of different alkyl-chain lengths. The resulting panthenol monoester (PME) has amphipathic properties. This strategy provides an assortment of products with different physical-chemical properties, depending on the fatty acid involved in the reaction.
Enzymatic synthesis of panthenol monoacyl esters (PMEs)
Proof-of-concept experiments are currently being carried out to validate the process and products obtained at a laboratory scale.
Benefits:
- The reactions are solvent-free and take place in mild conditions, which makes them not toxic, improves sustainability, and reduces costs.
- The substrates uses and their biocatalytic transformation are natural, and so the resulting products.
- The synthesis protocol is in one step. It provides high yield and selectivity, improving productivity.
- The process allows for easy recovery of biocatalysts and reuse, which means more cost savings.
- The synthesis provides an assortment of products with different physical-chemical properties.
The represented institution is looking for a collaboration that leads to commercial exploitation of the presented invention.
Institution: Universidad de Murcia, Universitat Jaume I
TRL: 3-4
Protection status: Spanish Patent Application and PCT extension
Financed: Proyectos de Prueba de Concepto (Agencia Estatal de Investigación)
Contact: Noelia Mas / tech@viromii.com