Currently, ischemic stroke is one of the leading causes of long-term disability in the world. In this regard, providing an early treatment is crucial to minimize the risk of serious brain damage and prevent subsequent disabilities. The best treatment for acute ischemic strokes nowadays consists of restoration of blood flow with thrombectomy, which can be performed in conjunction with the administration of intravenous thrombolytic medication, such as the tissue plasminogen activator (tPA). However, this approach presents obstacles such as the high number of patients that are excluded from recanalization therapies and the fact that half of the patients who undergo a thrombectomy combined with the administration of tPA are still disabled three months after stroke. All these factors have underlined the need to develop new alternative methods for the treatment of ischemic stroke.
In this context, researchers from the Instituto de Biomedicina de Sevilla (IBiS) and Hospital Universitario Virgen Macarena have developed a cell suspension based on bone marrow-derived cells that can be used for the treatment or amelioration of ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke patients. The researchers have developed a cell suspension of autologous adult bone marrow-derived mononuclear cells (BM-MNCs) for the treatment of ischemic stroke. This suspension is administered into the stroke related area via intra-arterial application, thus increasing the direct contact with endothelial cells.
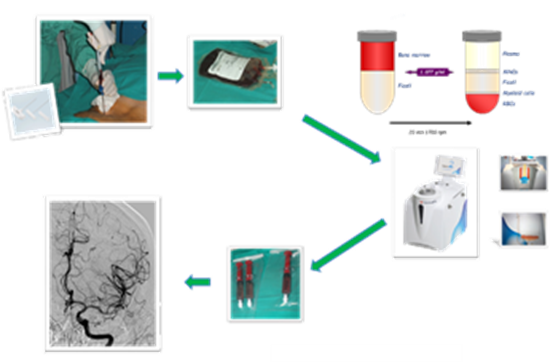
The inventors have assessed the safety and efficacy of the developed cell suspension of autologous BM-MNCs transplantation in a phase IIb clinical trial. In said trial, two different doses of BM-MNCs were tested on acute patients with middle cerebral artery (MCA) ischemic stroke. The obtained results indicated that the transplantation of autologous BM-MNCs was associated with improved outcomes, as evidenced by a higher proportion of patients achieving modified Rankin Scale (mRS) scores of 0–2 at 90 and 180 days.
Benefits:
- It is a highly safe treatment, as it involves an autologous transplant.
- The trials performed showed an improvement in axonal integrity of the patients.
- The technology allows to promote stroke recovery even in the acute phase.
- The cell suspension has been shown to increase the serum growth factors and cytokines, leading to an improved recovery of the subject.
- Intra-arterial administration of the suspension provides a feasible and less invasive method than intracerebral or intraventricular.
The represented institution is looking for a collaboration that leads to commercial exploitation of the presented invention.
Institution: Instituto de Biomedicina de Sevilla (IBiS) & Hospital Universitario Virgen Macarena
TRL: 3-4
Protection status: Patent Application
Contact: Carlos G. Gredilla / c.gredilla@viromii.com