Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is widely known for being a key molecule for human metabolism. This compound’s importance stems from its antioxidant activity, and it plays an essential role in processes such as cellular energy production. Furthermore, low levels of CoQ10 have been found in patients suffering from different pathologies such as cancer and various cardiovascular diseases.
Given the increasing cases of these diseases and the adverse effects of current therapies, researchers from Universidad Pablo de Olavide (UPO) have discovered the potential of using 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, also known as pHB, as an adjuvant for certain pathologies.
This molecule belongs to the synthesis route of CoQ10, acting as a precursor of said compound. The incubation of tumoral cells with pHB originates a change in their metabolism, causing an increase in their catabolic activity and reversing the Warburg effect.
The addition of pHB to tumoral cells modulates their mitochondrial activity, making them more sensitive to anti-cancer drugs, and increasing the specificity and effectiveness of the main treatment.
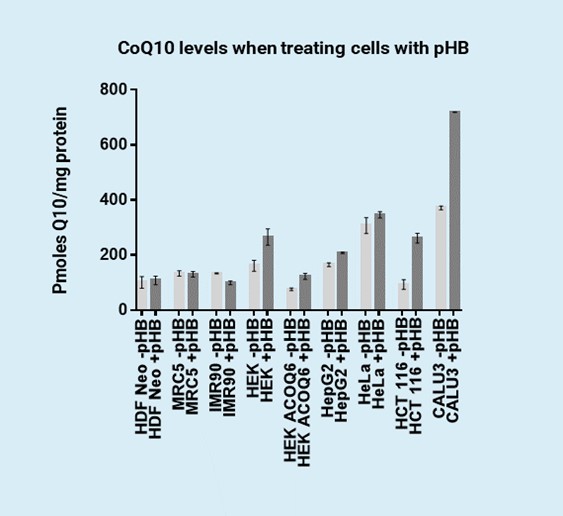
A Patent Application has been submitted in 2023 at the Spanish Patent and Trademark Office (OEPM). Additionally, the researchers have validated the efficiency of pHB in restoring the levels of CoQ10 in the various cell lines including HDF, MRC-5, HEK, or HCT 116.
Benefits:
- The molecule is non-toxic, given the fact that it’s an amino acid analog.
- The technology is effective and has been proven to increase the levels of CoQ10 in various tumoral cell lines.
- Supplementation with this molecule could reduce the necessary dose of main treatments, thus reducing the negative effects of these on patients.
- 4-hydroxybenzoic acid is distributed by well-known suppliers, which makes it easier to scale.
- The molecule is versatile and could be used in the treatment of several diseases that involve mitochondrial dysfunctions, such as cancer, cardiovascular, or neurodegenerative diseases. Furthermore, it can also be used to enhance metabolic processes, such as muscle development, in healthy individuals.
The represented institution is looking for a collaboration that leads to commercial exploitation of the presented invention.
Institution: Universidad Pablo de Olavide
TRL: 3-4
Protection status: Patent Application
Contact: Nuria Bas / nuria@viromii.com