Muscular dystrophies are a group of rare inherited genetic conditions, different types of mutations in the genes that control muscle structure and function gradually cause weakness and disability. Existing therapies for muscular dystrophies rely on physical procedures and drug-based treatments such as glucocorticoids, however with limited results and a risk of adverse effects. RNA-based therapies in development report encouraging data but still face important challenges in their effectivity in vivo, regulatory hurdles and high development costs.
Researchers from the Spanish Biomedical Research Networking Centre of Bioengineering, Biomaterials and Nanomedicine (CIBER-BBN) have found that that FDA approved drug for the treatment of hematologic malignancies bortezomib (VELCADE®) used together with a cell-adhesion adjuvant strongly increases myotubes regeneration, structures in which myoblasts are congregated. This is a novel strategy to develop therapies for neuromuscular diseases, based on the findings of the effect on muscle regeneration of the synergistic activation of the boron transporter and cell adhesion receptors, that stimulate multiple pathways and can compensate or by-pass damaged processes in these diseases.
The general formula of the pharmaceutical composition designed is:
- A boron compound.
- An adjuvant (such as fibronectin, specific cell adhesion peptide domains or mixture thereof, which constitute an adhesion zone for the myoblasts to migrate and multiply).
- Pharmaceutical excipients or other support elements to help its presentation and/or administration.
The synergistic activation of the boron transporter and the adhesion cell receptors promotes myotube formation, increases myotube diameter and suppresses cell mortality. In addition, the use of ultralow doses of boron compounds suppresses cell mortality associated with high-dose toxicity while ensuring safety and effectivity. The invention is designed to be administered in multiple forms: as an injectable or intramuscular solution, an oral composition drug or a topical composition drug.
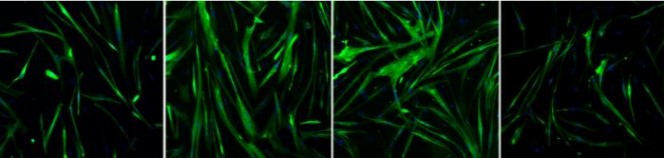
Properties and benefits have been thoroughly tested with different in vitro assays with human cells. In vivo assays were performed in mice, assessing their biocompatibility and muscle regeneration effects.
Benefits:
- Minimizes the effect of defective mRNA, allowing the correct differentiation of myoblasts.
- Possibility to implement approved boron compounds in its formulation.
- Minimize the dosage of boron compound while improving safety by reducing its toxicity.
- Highly adaptable administration method.
- Further skeletal muscle regeneration by deterring myotube degradation and promoting myoblast growth and differentiation.
The represented institution is looking for a collaboration that leads to commercial exploitation of the presented invention.
Institution: Spanish Biomedical Research Networking Centre of Bioengineering, Biomaterials and Nanomedicine (CIBER-BBN)
TRL: 3-4
Protection status: Spanish Patent Application
Contact: Noelia Mas / noelia@viromii.com