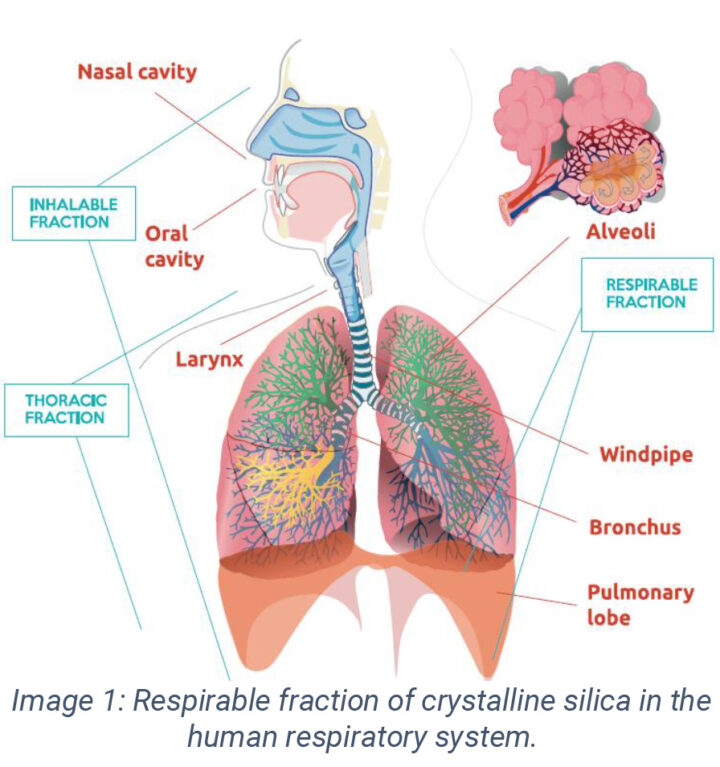
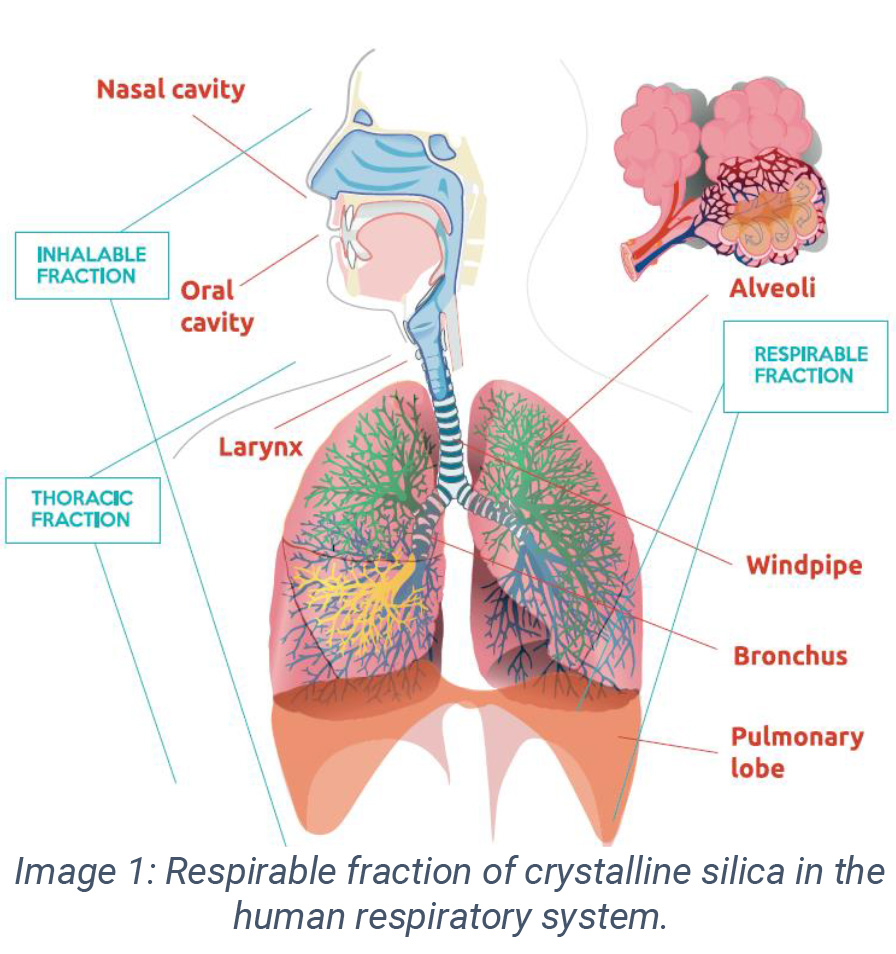
Crystalline silica comes in several forms, with quartz being the most common. Exposure to tiny particles of airborne silica, primarily quartz dust, occurs mainly in industrial and occupational settings. When inhaled, these particles can penetrate deep into the lungs. Breathing crystalline silica dust can cause silicosis and lung cancer, which in severe cases can be disabling, or even fatal. European legislation has included RCS -Respirable Crystalline Silica- within carcinogens and mutagens in the workplace. One of the European Union’s efforts to make respirable silica safer in manufacturing processes was the SILICOAT project.
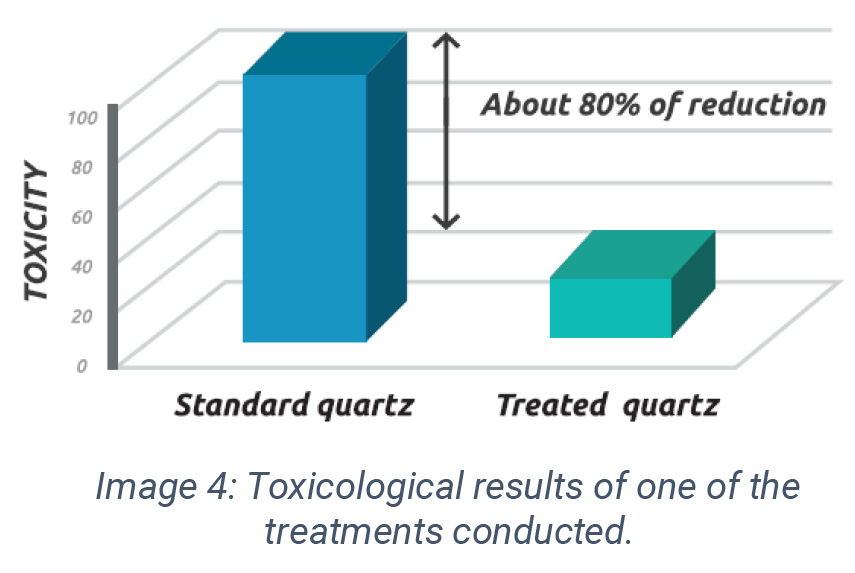
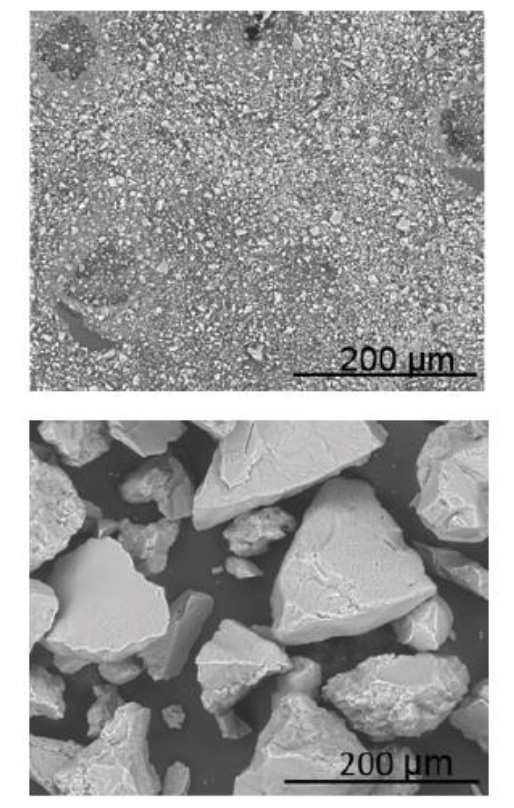
In this project, carried out between 2011 and 2014, it was developed a coating technology that proved to be effective in reducing RCS toxicity at manufacturing processes involving wet stages. However, there’s RCS exposure in industrial processes that do not involve wet stages. In those processes, this solution was not adequate.
Institution: Universitat Jaume I
TRL: 7-8
Protection status: Patent application
Contact: Laura Núñez / laura@viromii.com